Magnets are an essential part of our daily lives, from simple fridge magnets to advanced applications in various industries. The discovery of the world’s strongest magnets, known as neodymium magnets, has revolutionized several industries by enabling new technologies and improving existing processes. In this article, we will explore the top 5 industries that have been transformed by the use of these powerful magnets.
1. Renewable Energy
The renewable energy sector has witnessed significant advancements with the implementation of neodymium magnets. Wind turbines, for instance, rely on these strong magnets to convert kinetic wind energy into electrical energy. The magnets are used in the generator’s rotor, which rotates when the wind turbine blades turn. This rotation generates a magnetic field that induces an electrical current in the stator windings, producing electricity.
Neodymium magnets are preferred in wind turbines due to their high magnetic strength, which allows for the use of smaller and lighter generators. This, in turn, reduces the overall weight and cost of wind turbines, making them more efficient and cost-effective.
Additionally, neodymium magnets are also used in electric vehicles (EVs) to power their motors. The magnets are incorporated into the motor’s rotor, which generates a magnetic field that interacts with the stator’s coils to produce torque and propel the vehicle. The high magnetic strength of neodymium magnets enables the creation of smaller, more powerful motors that consume less energy, making EVs more efficient and environmentally friendly.
2. Medical Technology
The medical industry has also benefited from the use of neodymium magnets, particularly in the field of medical imaging and diagnostics. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scanners, for example, rely on the strong magnetic fields generated by neodymium magnets to produce detailed images of the human body.
MRIs use a large, powerful magnet to create a strong magnetic field that aligns the protons in the body’s hydrogen atoms. Radio waves are then pulsed through the field to cause the protons to emit signals, which are detected by the MRI machine and used to construct high-resolution images of the body’s internal structures.
Neodymium magnets are essential in MRIs due to their ability to generate extremely strong and uniform magnetic fields. This allows for clearer and more detailed images, which in turn helps medical professionals make more accurate diagnoses and develop more effective treatment plans.
3. Manufacturing and Robotics
The manufacturing industry has seen significant improvements in efficiency and productivity thanks to the implementation of neodymium magnets in robotics and automation systems. These magnets are used in robotic arms and grippers, allowing for precise and forceful manipulation of small and delicate components.
The strong magnetic fields generated by neodymium magnets enable robotic arms to maintain a firm grip on objects while also allowing for precise positioning and movement. This is especially beneficial in industries such as electronics and semiconductor manufacturing, where components are often small and sensitive, requiring precise handling to avoid damage.
In addition to robotics, neodymium magnets are also used in other manufacturing processes, such as magnetic levitation (maglev) systems for material handling and transport. These systems use the magnetic repulsion force between neodymium magnets to levitate and move objects without the need for physical contact, reducing friction and wear on components.
4. Aerospace
The aerospace industry has also been impacted by the advent of neodymium magnets, particularly in the areas of propulsion and navigation. For example, neodymium magnets are used in the development of high-performance electric propulsion systems for satellites and spacecraft.
These systems rely on the strong magnetic fields generated by neodymium magnets to accelerate charged particles, creating thrust without the need for traditional chemical propellants. This not only reduces the overall mass of spacecraft but also increases their efficiency and maneuverability.
Neodymium magnets are also used in the navigation systems of spacecraft and satellites. These systems, known as attitude determination and control systems (ADCS), use neodymium magnets in combination with sensors and actuators to determine the orientation and position of a spacecraft in space. This information is then used to adjust the spacecraft’s orientation and maintain its desired trajectory.
5. Data Storage and Computing
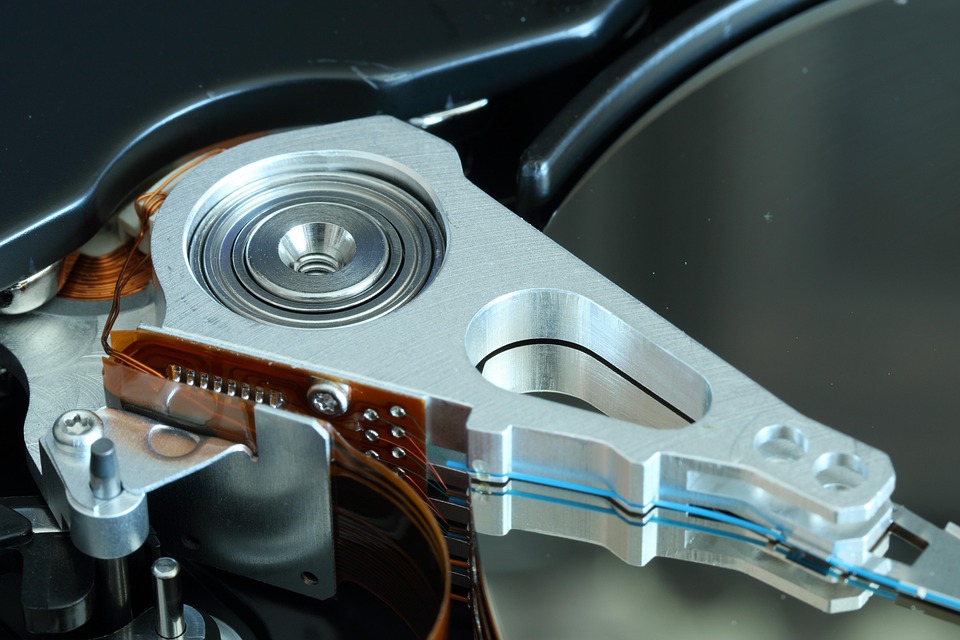
The development of neodymium magnets has also had a profound impact on the data storage and computing industries. Hard disk drives (HDDs) in computers and data centers rely on neodymium magnets to store and retrieve large amounts of data.
In an HDD, a spinning disk coated with a magnetic material, called the platter, is used to store data. The data is stored as a series of magnetic patterns, which are created and read by a read/write head that contains a small neodymium magnet. The strong magnetic field generated by the neodymium magnet allows the read/write head to accurately record and retrieve data from the platter.
Neodymium magnets are essential in HDDs due to their high magnetic strength, which allows for the storage of more data in a smaller area. This, in turn, has enabled the development of smaller, more efficient data storage devices with increased storage capacities.
Conclusion
The discovery and widespread adoption of neodymium magnets have revolutionized various industries across the globe. From renewable energy and medical technology to manufacturing, aerospace, and data storage, these powerful magnets have enabled new technologies and significantly improved existing processes.
As researchers continue to explore the capabilities of neodymium magnets and develop even stronger materials, it is likely that their applications will expand even further, leading to further innovations and advancements in a wide range of industries.
FAQs
1. What makes neodymium magnets so strong?
Neodymium magnets, also known as neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) magnets, are composed of an alloy of neodymium, iron, and boron. It is the unique combination of these elements and their specific atomic arrangements that give neodymium magnets their exceptional magnetic strength.
2. Are neodymium magnets safe for humans?
While neodymium magnets are generally considered safe for use in consumer and industrial products, they can pose risks if not handled properly. Magnets should be kept away from small children, who may swallow them, leading to serious health complications. Additionally, handling large or powerful magnets without proper training or safety equipment can result in injury due to their strong magnetic fields and attractive forces.
3. Are neodymium magnets environmentally friendly?
Neodymium magnets are made from rare earth elements, which are mined from the earth. The mining process can have environmental impacts, such as habitat destruction and pollution. However, many manufacturers are adopting more sustainable mining practices and recycling methods to minimize the environmental impact of neodymium magnet production.
4. How expensive are neodymium magnets compared to other magnets?
Neodymium magnets tend to be more expensive than ferrite or alnico magnets due to their higher rare earth element content and the more complex manufacturing process required to produce them. However, their exceptional magnetic strength often compensates for their higher cost, as smaller and fewer neodymium magnets can achieve the same performance as larger and more numerous ferrite or alnico magnets.
5. Can neodymium magnets be recycled?
Yes, neodymium magnets can be recycled. In fact, recycling neodymium magnets is becoming increasingly important due to the growing demand for rare earth elements and the environmental impacts of mining them. Recycling processes for neodymium magnets are being developed and refined to recover valuable rare earth elements and reduce the need for new mining operations.